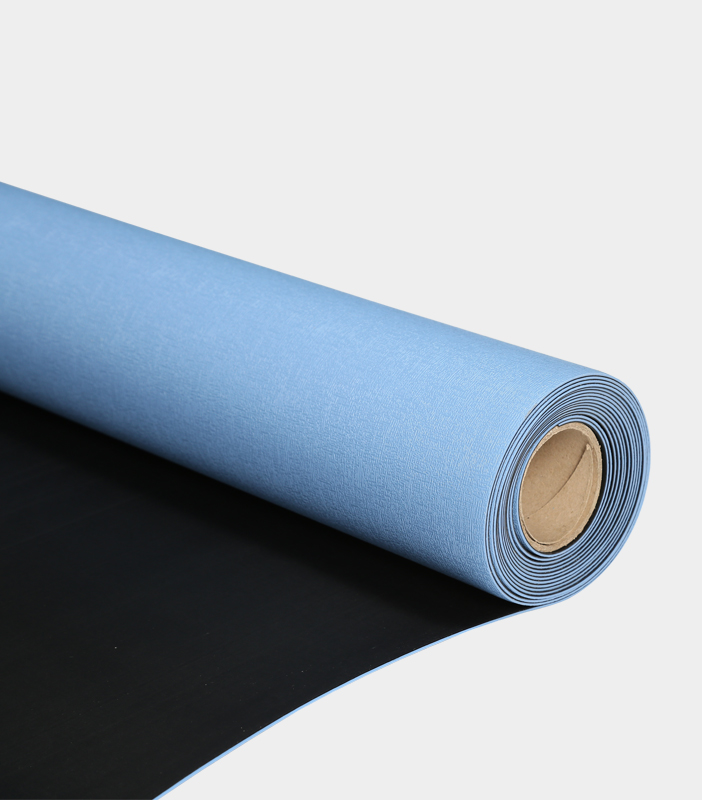
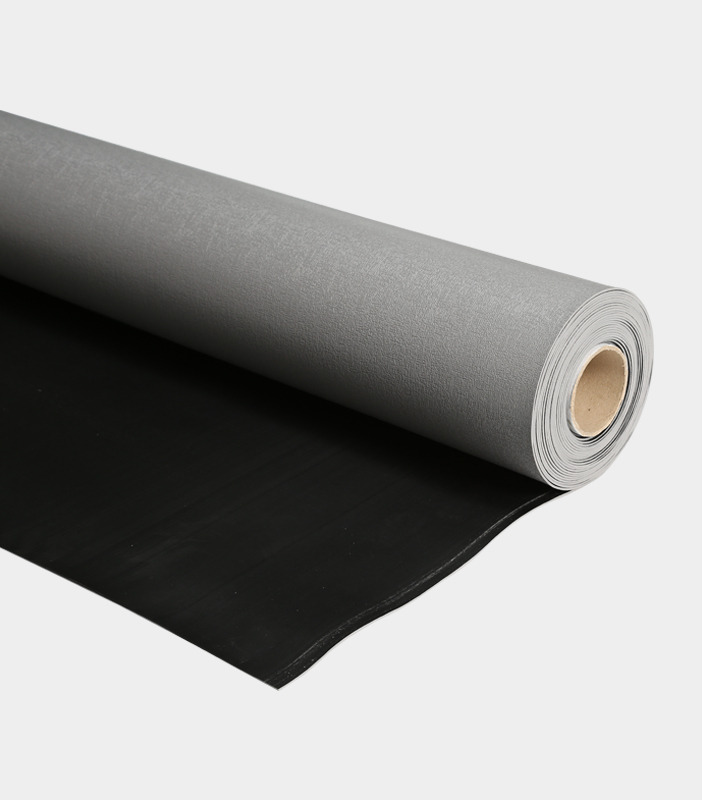
Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats are essential components in environments where electrostatic discharge (ESD) control is critical to protect sensitive electronic components and devices during assembly and testing. To ensure effective static control, these mats are designed using specific materials and technologies.
1. Conductive Rubber or Vinyl:
Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats are typically constructed from conductive materials like rubber or vinyl. These materials contain conductive additives that allow them to efficiently dissipate static charges. The choice between rubber and vinyl often depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired durability.
2. Conductive Layers:
Many ESD Table Mats feature multiple layers, including a conductive layer. This conductive layer helps evenly distribute static charges across the mat's surface, preventing the build-up of potentially harmful charges.
3. Static-Dissipative Layers:
In addition to conductive layers, some mats incorporate static-dissipative layers. These layers have a higher resistance than conductive layers, allowing them to dissipate static charges more slowly. This controlled dissipation is suitable for areas where rapid discharge may not be ideal.
4. Carbon-Fiber Reinforcement:
Some Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats include carbon-fiber reinforcement. Carbon fibers enhance conductivity and help maintain a consistent level of resistance across the mat's surface. This reinforcement ensures that the mat remains effective even with prolonged use.
5. Grounding Points:
To be effective, Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats need to be grounded. They come equipped with grounding points that allow them to be connected to the facility's grounding system. Proper grounding ensures that static charges are safely discharged.
6. Static Dissipative Top Layers:
The top surface of Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats often consists of a static-dissipative layer. This layer provides a safe and controlled work surface for sensitive components and devices. It prevents tribocharging, which occurs when two materials rub together and generate static charges.
7. Permanently Conductive Layers:
Some mats have permanently conductive layers, meaning they maintain their conductivity throughout their lifespan. This ensures consistent ESD protection, as the conductivity doesn't degrade over time.
8. Ultraviolet (UV) Stabilization:
Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats are often exposed to light, especially in manufacturing environments. UV stabilization is a technology used to prevent the degradation of the mat's surface due to UV exposure. This technology extends the mat's lifespan and ensures its continued effectiveness.
9. Heat Resistance:
In environments where soldering or hot air rework stations are used, heat resistance is a crucial feature. Many Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats are designed to withstand high temperatures without warping or losing their ESD properties.
10. Easy-to-Clean Surfaces:
Maintaining a clean and contamination-free workspace is essential in electronic assembly. Some mats have easy-to-clean surfaces that resist the build-up of dust and debris, ensuring that the work area remains clean and static-free.
Electronic Assembly ESD Table Mats employ a combination of materials and technologies to ensure effective static control in environments where sensitive electronic components are handled. These mats are designed to prevent static charge build-up, protect sensitive devices, and maintain a safe and controlled work environment. By utilizing conductive and static-dissipative materials, carbon-fiber reinforcement, grounding points, and UV stabilization, these mats contribute significantly to the protection of valuable electronic equipment and the prevention of costly ESD-related damage.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English España
España Deutsch
Deutsch